By Abhilash Kumar
- Spotify continues to be the market leader and recorded a 23% YoY growth in total revenue during CY 2019.
- Music streamers are focusing on creating exclusive content with podcasts continuing to feature strongly in 2020.
Seoul, Hong Kong, New Delhi, Beijing, London, Buenos Aires, San Diego – 3rd April 2020
Global online music streaming subscriptions grew 32% year-on-year (YoY) reaching 358 million subscriptions in CY 2019, according to the latest findings from Counterpoint Research. This is driven by the availability of exclusive content like podcasts, originals which attracted people towards the platform and eventually turned them as subscribers. Also, promotional activities like price cuts in subscriptions in emerging markets, bundled offers from telcos added to the growth. We expect that online music streaming subscriptions to grow more than 25% YoY to exceed 450 million subscriptions by the end of 2020.
Commenting on the overall market, Research Analyst, Abhilash Kumar, said, “Paid subscriptions grew 32% YoY compared to 23% YoY growth of total MAUs. This suggests people are ready to pay for music streaming for a hassle-free experience. However, this is not completely user-driven. Music streaming platforms are following a two-step approach to gain subscribers, first registering them to their platform as free users by means of excellent advertising campaigns and secondly pitching them with attractive offers to transfer them to become paying subscribers.”
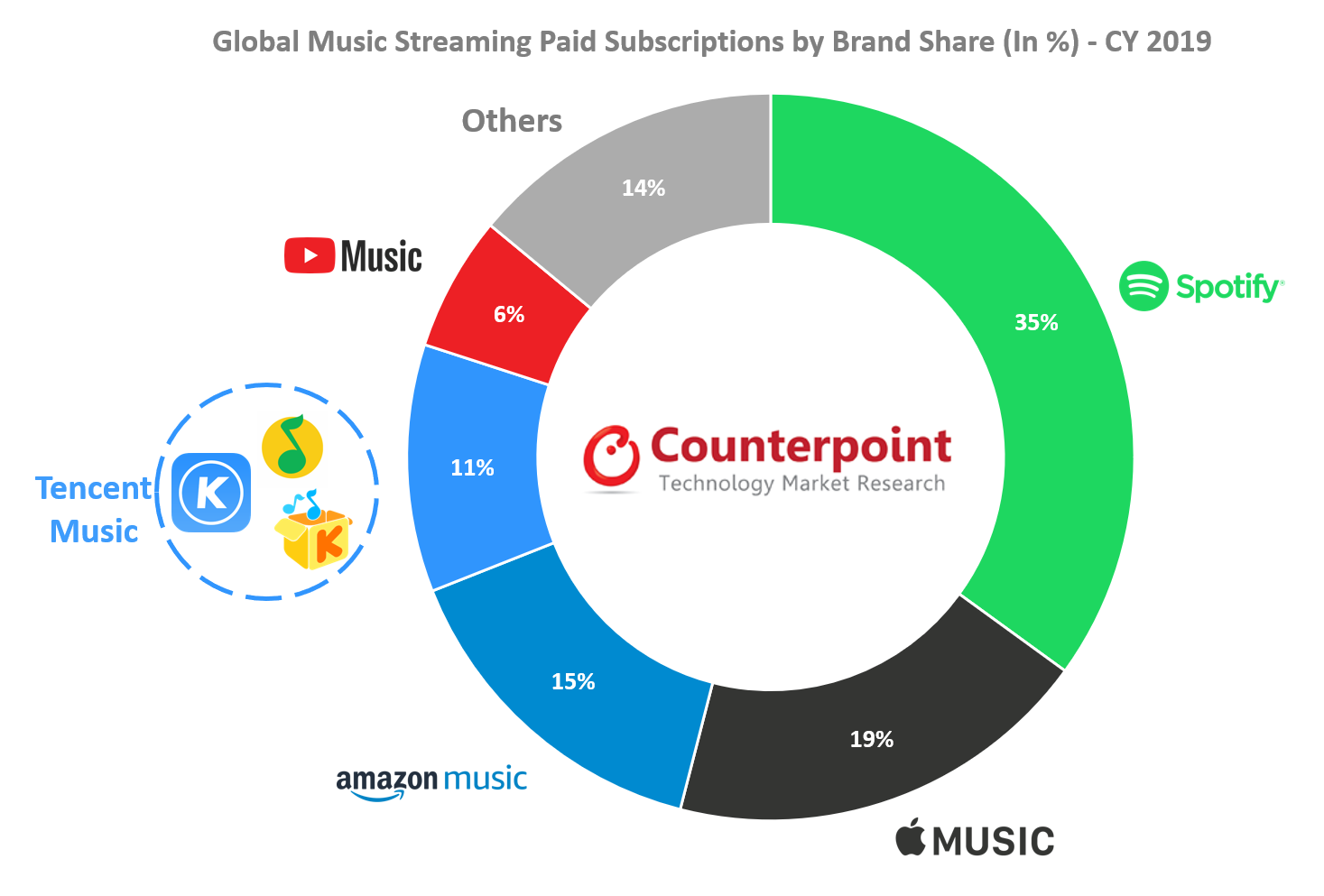
Spotify topped CY 2019 grabbing a 31% share of the total revenue and a 35% share of the total paid subscriptions. The runner up, Apple Music, follows with a 24% share of total revenues in the industry and a 19% share of the total paid subscriptions. Due to Apple’s high focus on its services segment which includes Apple Music, its subscription base grew 36% YoY in CY 2019. Amazon Music subscriptions reached a 15% share in 2019 compared to 10% in 2018.
Talking about the top performers, Kumar added, “Spotify maintained its top spot with the help of promotional activities like free Spotify Premium for three months, price cuts, customized campaigns like Spotify and a focus on exclusive content. Tech giants like Amazon, Apple, Google have started focusing on music streaming and have sufficient cash at their disposal to give stiff competition to Spotify. Apple Music is making improvements in its app like the introduction of night mode, curated playlists to target a group, etc. Similarly, Amazon Music has been trying lossless music and is creating its own niche where it competes with Tidal.”
Despite global players strongly pushing their music streaming platforms, regional players stand strong in their respective regions, primarily because of regional exposure and high focus on local content. Gaana continues to be the no.1 player in the Indian market, Yandex Music is leading in Russia. Similarly, Anghami leads the Arab world. Tencent Music Group leads the China market with the help of its apps QQ Music, Kugou and Kuwo.
Discussing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the OTT industry, Kumar added, “We expect the OTT sector will experience an uptick as people stay at home actively tracking the latest updates. During this outbreak, audio OTT consumption has switched from music streaming to the radio. People in highly affected areas are worried about the outbreak and are therefore continuously tuned to news on TV/radio for updates. The traction of news channels and podcasts saw an upswing while that for music streaming dropped.”
What’s common is that both the regional and global players are focusing a lot on building exclusive content. Acquiring podcast companies and creating their own channels are all being undertaken. It’s often exclusive content that drives paid subscription growth.
More than 80% of music streaming revenue came from paid subscriptions. The rest came from advertisements and partnerships with brands and telcos. Therefore, increasing paid subscriptions is of prime importance for music streaming platforms.
The comprehensive and in-depth chain of reports on Global Online Music Streaming Market for Q4 2019 is available to help track the market in terms of MAUs by region, paid subscriptions by region, revenues, and ARPU. To view the global report in terms of users, revenues and ARPU, click here. For regional analysis on MAUs and paid subscriptions, click here. Please contact press(at)counterpointresearch.com for further questions regarding our in-depth research, insights or other press inquiries.
Background:
Counterpoint Technology Market Research is a global research firm specializing in Technology products in the TMT industry. It services major technology firms and financial firms with a mix of monthly reports, customized projects and detailed analysis of the mobile and technology markets. Its key analysts are experts in the industry with an average tenure of 13 years in the high-tech industry.

Click HERE to visit or return to jeeni.com



